
The History and Development of Smart Home Systems
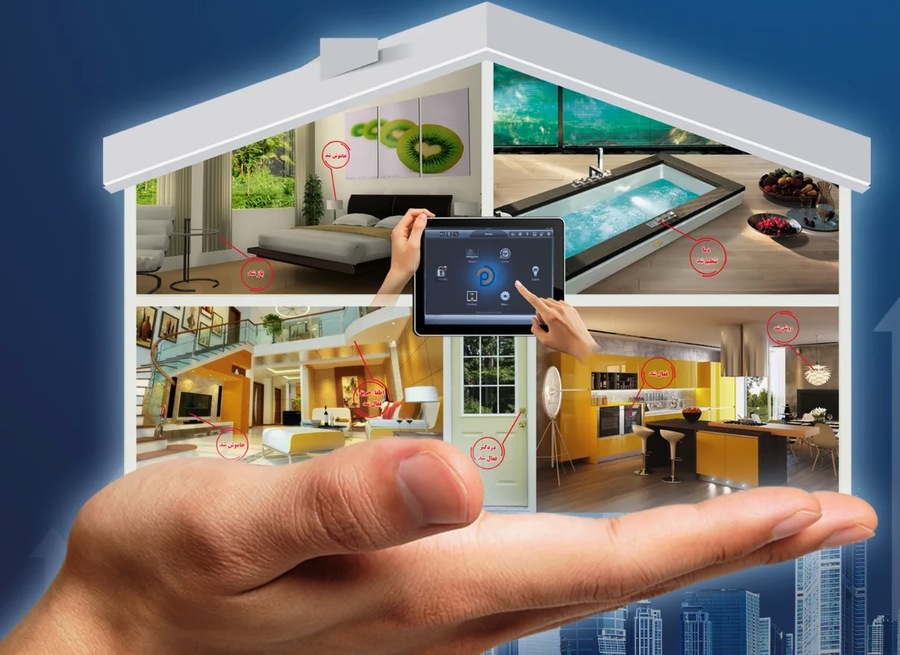
Home automation, commonly referred to as a smart home, encompasses a system of interconnected devices capable of performing tasks and solving everyday problems without human intervention. These systems can manage actions such as automatically switching lights on and off, adjusting heating or air conditioning, and notifying homeowners of intrusions, fires, or water leaks. Smart home technology is considered a subset of the Internet of Things (IoT), which includes any internet-connected device. However, smart homes specifically involve household devices accessible via the internet, enhancing convenience, security, and energy efficiency. For expert installation and integration of smart home systems, Awal Experts provides top-notch services to ensure your home is equipped with the latest technology.
Early Innovations in Home Appliances
The journey toward modern home automation began with the invention of household appliances that used electricity for cooking and cleaning tasks. Significant milestones include:
– Vacuum Cleaner (1901): Revolutionized cleaning by making it easier and faster to clean large areas.
– Toaster (1909): Simplified breakfast preparation with a convenient way to toast bread.
– Home Refrigerator (1913): Provided a reliable method for food preservation, extending the shelf life of perishable items.
– Dishwasher (1913): Reduced the time and effort needed for washing dishes, making kitchen cleanup more efficient.
– Temperature-Controlled Iron (1927): Improved the ironing process with better control over temperature settings.
– Garbage Disposer (1927): Offered a convenient way to dispose of kitchen waste, reducing the need for frequent trash disposal.
– Washing Machine (1935): Greatly reduced the labor involved in laundry, freeing up time for other tasks.
– Dryer (1935): Complemented the washing machine by providing a quick way to dry clothes.
– Microwave Oven (1945): Introduced a fast and convenient method for cooking and reheating food.
– Rice Cooker (1945): Simplified the process of cooking rice to perfection.
– Electric Coffee Maker (1952): Made brewing coffee quick and convenient, contributing to the popularity of home-brewed coffee.
These innovations laid the groundwork for more advanced automation by introducing the concept of electric household assistance.

Early Attempts at Home Automation
In the mid-20th century, the first isolated attempts at home automation appeared. These early systems, although rudimentary by today’s standards, paved the way for future developments. Notable examples include:
– Push-Button Manor (1950): Created by American engineer Emil Mathias, this house featured buttons throughout that automated basic household tasks. For its time, it seemed futuristic and highlighted the potential of home automation.
– Echo IV Computer (1966): Developed by American engineer James Sutherland, this computer could control climate equipment, manage appliance operations, and print shopping lists. It represented one of the earliest attempts at integrating computing technology with home management.
Development of Home Automation Standards
The first dedicated home device control standard, X10, was developed by Pico Electronics of Scotland in 1975. X10 utilized regular electrical networks to transmit signals, enabling the control of devices and lights remotely. This system’s affordability and ease of installation contributed to its widespread adoption.
X10 facilitated the remote control of appliances, lights, and other household devices using a combination of radio frequency and power line communication. It set the stage for future advancements by demonstrating the potential of a standardized approach to home automation.
In the 1980s, the United States became the primary market for X10 systems, while Europe saw limited use due to regulatory constraints. European companies eventually developed their own standards, including:
– European Installation Bus (EIB, 1990): Led by German companies, including Siemens, this standard aimed to unify the fragmented home automation market in Europe.
– BatiBus: Developed by a consortium led by French Electricité de France, BatiBus was another attempt to standardize home automation technology in Europe.
– European Home Systems Association (EHSA, 1991): Formed by companies like Philips, Daimler Benz, Thomson Consumer Electronics, and British Telecom, EHSA worked on creating a unified standard called European Home Systems (EHS).
In 1999, these companies agreed to merge their standards into a single protocol, KNX, which was introduced in 2002 and became open, facilitating broader adoption and innovation.
The Rise of the Term “Smart House”
In 1984, the National Association of Home Builders coined the term “smart house” to describe homes utilizing automation. This term captured the imagination of the public and the industry, symbolizing a future where homes could intelligently manage various tasks and improve quality of life. The concept gained mainstream attention with the release of Disney’s film Smart House in 1999, which popularized the idea of automated living spaces.
Advancements in Smart Home Technology
The 2010s marked a revolution in home automation, driven by the advent of smartphones. These pocket-sized computers provided an ideal platform for controlling smart home devices, leading to significant advancements in the technology. Key developments included:
– Dropcam Security Camera (2010): An affordable ($200) camera offering online video access and cloud storage. This product made home security accessible to a wider audience, allowing homeowners to monitor their properties remotely.
– Nest Thermostat (2011): A self-learning, smartphone-controlled thermostat addressing the complexity of previous programmable models. The Nest thermostat not only learned user preferences but also helped save energy by optimizing heating and cooling schedules. Google acquired Nest in 2014, further boosting its development and integration with other smart home products.
– Philips HUE Lighting System (2012): Featuring lamps with adjustable brightness and spectrum, each equipped with a ZigBee radio interface. This system allowed users to create customizable lighting environments controlled via smartphones or voice commands.
– SmartThings Automation System (2012): Offering a hub for $100, sensors for $30-40, and a wide range of compatible devices. SmartThings’ open platform supported over 100,000 third-party devices and applications from 8,000 developers. Samsung acquired SmartThings in 2014, enhancing its reach and capabilities.
– Amazon Echo (2014): The first smart speaker with Alexa, allowing voice-controlled home device management. The Amazon Echo provided users with a convenient way to interact with their smart home systems using natural language. Google and Apple followed with Google Home (2016) and Apple HomePod (2017), respectively, each featuring their own smart assistants. Xiaomi introduced the XiaomiMi AI Speaker in 2017, offering similar functionality at a competitive price point.
Modern Smart Home Systems
Today, smart home systems are continually evolving, offering capabilities such as remote control of lights, climate management, and security monitoring. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further enhanced the functionality and convenience of these systems. Homeowners can now enjoy a seamless and personalized living experience, with smart home devices working together to anticipate their needs and preferences.
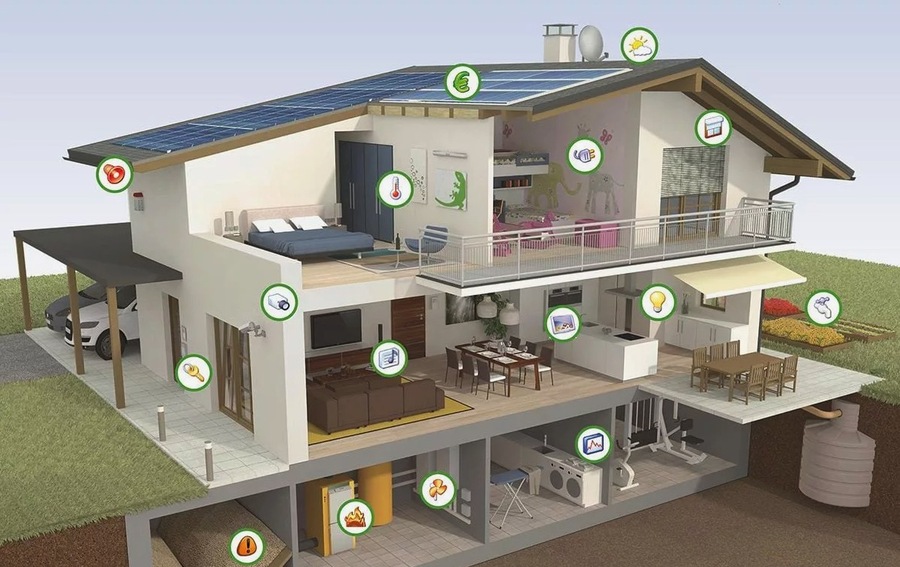
The Role of Professional Services in Smart Home Integration
To fully realize the benefits of smart home technology, it is essential to have a well-designed and properly installed system. Professional services, such as those offered by Awal Experts in Dubai, provide expert installation and maintenance, ensuring seamless and efficient smart home experiences for users. Awal Experts specialize in integrating various smart home components, from lighting and climate control to security and entertainment systems, delivering a cohesive and reliable solution for modern living.
Conclusion
The development of smart home systems has come a long way since the early days of electrical household appliances. From the initial innovations of the 20th century to the sophisticated, interconnected devices of today, home automation has transformed the way we live. With continuous advancements in technology and increasing accessibility, the future of smart homes looks promising, offering even greater convenience, security, and efficiency for homeowners around the world.

Soccer lover, loves to cook, guitarist. Specializes in administrative technology and is responsible for educating other employees on using progressive systems and applications.